Windows laptops sometimes struggle with battery life due to resource-intensive applications running in the background. Fortunately, Windows Task Manager includes useful power monitoring tools to help identify these battery-draining apps.
How to Access Power Usage Data
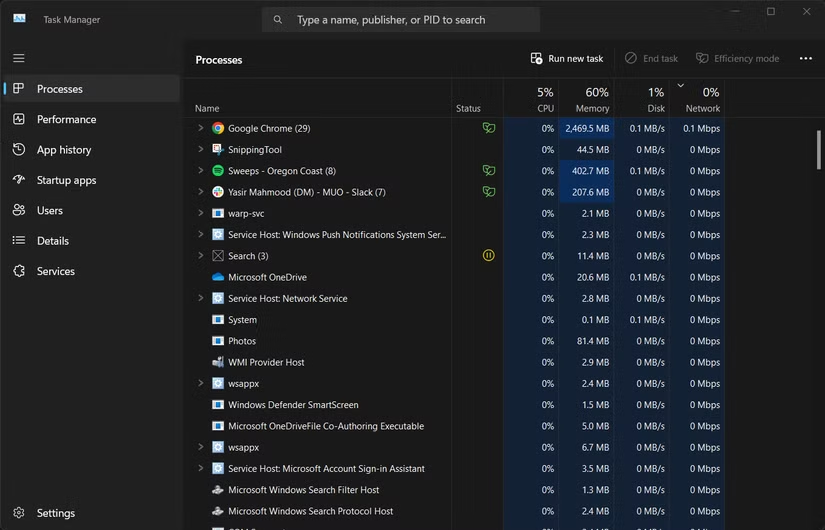
Finding battery-draining apps in Windows 11 is easy because Task Manager offers detailed power usage statistics. There are several ways to open Task Manager:
- Right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete and select Task Manager.
- Type “Task Manager” in the Windows search bar.
If you’re having trouble getting Task Manager to open or function properly, check out our guide on how to fix the Task Manager if not working in Windows before proceeding.
Once Task Manager is open, follow these steps to see power usage data.
- Click More details to see multiple tabs if you see a simplified view.
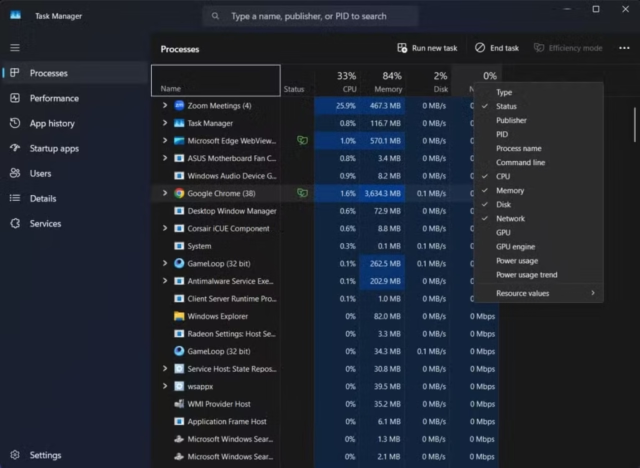
- Navigate to the Processes tab at the top—this shows the power usage data.
- By default, Task Manager might not display the power usage columns; Right-click on any column header in the process list.
- Select Power usage and Power usage trend from the context menu.
- Wait a moment for Windows to gather and display the power data.
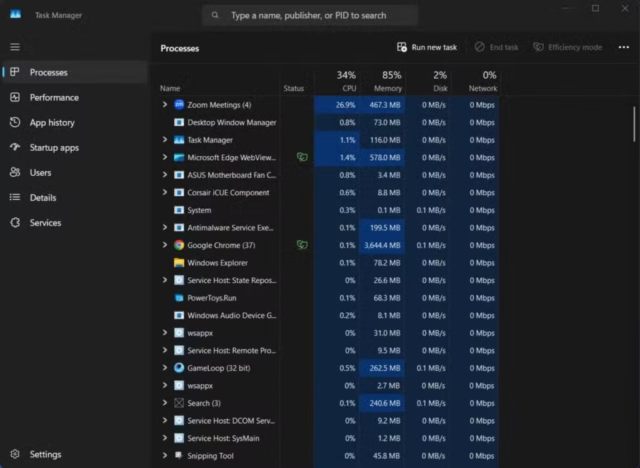
These columns show which applications demand the most energy from your battery. They are rated based on Very low, Low, Moderate, High, or Very high power consumption ratings.
What “Very High” Really Means for Your Laptop’s Battery
When Task Manager labels an application with “Very high” power usage, it’s essentially raising a red flag about your battery life. This rating doesn’t just mean the app is using more power than others; it usually indicates a significant drain that could reduce your laptop’s runtime by hours.
I’ve found that a single app with “Very high” power usage can sometimes drain your battery up to 2-3 times faster than usual. For example, a laptop that typically lasts 6 hours might only reach the 2-hour mark with resource-intensive applications running.
These power-hungry apps usually consume energy in one of three ways: heavy CPU processing, constant GPU usage, or continuous background activity. Video editing software, modern games, and some browsers with multiple tabs all fall into this category. Even worse are applications that continue high power consumption when minimized.
The “Power usage trend” column provides additional context by showing whether the app consistently uses high power or has just had a temporary spike. This distinction helps you identify the true battery drainers versus momentary resource hogs.
These Apps Are Probably Killing Your Battery
Several common applications frequently show up as battery hogs. Web browsers top the list—Chrome, with multiple tabs open, is a particularly battery-hungry app. While most modern browsers have improved their energy efficiency, they can still lead to an inaccurate battery estimate if left unchecked.
Video conferencing software like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet are also notorious power consumers. These apps use your camera and microphone and must maintain constant internet connections simultaneously. So it’s no wonder they drain batteries quickly during long virtual meetings.
Cloud synchronization tools like OneDrive, Dropbox, and Google Drive can silently sap your battery, too, especially during large file uploads or downloads. Even when they appear inactive, they might be working in the background.
Gaming and media applications are other obvious culprits. However, many of us don’t realize how much power video streaming services consume. If battery life is critical, consider using browsers with battery power-saving modes when watching videos online.
Surprisingly, many pre-installed Windows utilities can be power-hungry too. Search indexing, Windows Update, and even some antivirus solutions might show High or Very high power usage during certain operations.
Take Action Against Power-Hungry Apps
Once you’ve identified the battery-draining apps, it’s time to take control. For browsers, consider limiting the number of open tabs and extensions. You’d be amazed how much battery life you can reclaim by simply closing unused tabs—something worth remembering when wondering why your laptop battery never lasts as long as advertised.
You should consider changing the settings of applications that run in the background. Many apps automatically launch at startup and continue running silently.
Go to Settings> Apps> Startup to turn off non-essential startup applications and prevent them from draining your battery.
You can also use Windows built-in power settings. Click on the battery icon in the taskbar and adjust the power mode slider. Battery saver or Better battery modes limit background activity and reduce performance slightly to extend runtime considerably.
For critical battery situations, don’t hesitate to end the task for power-hungry applications. Right-click on the application in Task Manager and select End task when you need immediate battery relief. This pairs well with improving your laptop’s charging speed to regain full power quickly.
Another option could be to use web apps instead of desktop applications when possible. Many services offer lightweight web versions that consume significantly less power than their desktop counterparts.
Windows Task Manager provides useful insights into which apps are draining your battery more. You should regularly check power usage statistics to extend your laptop’s runtime between charges. Remember to adjust your usage habits based on your power situation—save the intensive tasks for when you’re plugged in.